Fundamentals of Ad Tech for AVOD Services
Last Updated on May 21, 2025 by Anjana Devi
With everyone wanting more stuff to watch online, ad-supported video-on-demand (AVOD) steps in with a big library of content at no cost. They use data to show you ads and suggest things you might like. While subscription services get a lot of attention, AVOD offers a free option for those who don’t want to pay.
AVOD allows streaming platforms to generate revenue without solely relying on subscription fees, thus offering users an alternative way to access content for free. This broader accessibility can attract a larger audience, including those who may not be willing or able to pay for subscriptions.
Moreover, targeted advertising enhances the effectiveness of ads by showing them to users who are more likely to be interested, based on their demographics, interests, and viewing history. This not only improves the user experience by showing relevant ads but also increases the likelihood of engagement and conversion for advertisers, leading to higher ad revenues for the streaming platform
Understanding VAST
Designed by the Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB), (Video Ad Serving Template (VAST) tags are standardized XML documents that provide instructions for video players on how to display video ads. They serve as a communication bridge between ad servers and video players, ensuring that ads are displayed correctly across different platforms and devices.
How do VAST tags work?
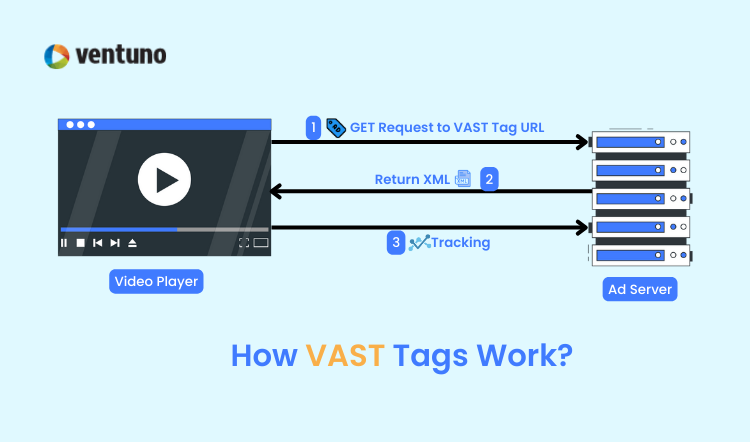
1. Sending a Request
Suppose you’re browsing a website, and the video player on the page needs to show an ad. It sends a request to a specific URL that’s set up to deliver ads. Let’s use an example URL: http://advertising.example.com/ads?params_here
2. Receiving the Response
The ad server responds with an XML document in a specific format called VAST (Video Ad Serving Template). It looks something like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<VAST version="2.0">
<Ad id="...">
<InLine>
<AdTitle><![CDATA[ad_title]]></AdTitle>
<Impression><![CDATA[tracking_pixel_url]]></Impression>
<Creatives>
<Creative sequence="1" id="300">
<Linear>
<Duration>00:00:10</Duration>
<MediaFiles>
<MediaFile type="video/mp4"><![CDATA[ad_url]]></MediaFile>
</MediaFiles>
</Linear>
</Creative>
</Creatives>
</InLine>
</Ad>
</VAST>
3. Parsing the Response
The video player reads this XML and extracts the necessary information, like the ad’s duration, title, tracking pixels for impressions, and the URL where the ad video is hosted.
4. Displaying the Ad
The player then displays the ad according to the instructions in the VAST response. It might show the ad before the video starts or during a break, depending on the content.
5. Tracking Events
Throughout the ad’s playback, the player may send requests to tracking servers specified in the VAST response. These requests indicate events like when the ad starts, completes, or when the user clicks on the ad.
What are Ad Pods?
Adpods are clusters of video ads that play sequentially during a commercial break within a streaming session.
Adpodding refers to the practice of grouping multiple ads together to be shown to viewers in a single interruption. This approach aims to enhance user experience by reducing the frequency of interruptions while allowing advertisers to convey their messages effectively.
Imagine you’re streaming a TV show online. Instead of being interrupted by individual ads throughout the program, you might encounter an adpod during designated commercial breaks. This adpod could include multiple ads from different advertisers played one after another, creating a more streamlined viewing experience.
Types of Ad Pods
Structured Ad Pods
Structured ad pods follow a predetermined sequence of ads that are played in a specific order. This type of ad podding allows advertisers to plan and coordinate their messaging effectively.
Dynamic Ad Pods
Dynamic ad pods are customized based on viewer behavior, preferences, and available ad inventory. Advertisers can tailor ad pods in real time to target specific audience segments or optimize ad delivery based on various factors.
Hybrid Ad Pods
Hybrid ad pods combine elements of both structured and dynamic ad podding. They may have a predefined sequence of ads but also incorporate dynamic elements to adjust the content based on viewer data or ad availability.
Strategies for Effective Podding
Optimizing Ad Placement
Place adpods strategically within the content to minimize viewer disruption while maximizing ad exposure and engagement.
Balancing Ad Frequency
Find the right balance between ad frequency and viewer experience to avoid overwhelming viewers with excessive ads.
Targeting and Personalization
Use viewer data to customize adpods, ensuring that ads are relevant and resonate with the target audience.
Testing and Optimization
Continuously test different ad pod configurations, sequences, and lengths to identify what works best for both viewers and advertisers.
Understanding Direct Assets
Direct assets are video advertisements that you directly upload into your Content Management System (CMS).
By opting to upload your own ads, you gain significant advantages:
1. Control Over Content
By directly uploading your ads, you retain complete control over their content, ensuring they resonate with your brand identity and messaging without any external alterations. This control guarantees that the ads seamlessly align with your streaming service’s content and user experience.
2. Cost Savings
By bypassing advertising agencies or intermediaries, you avoid paying commissions or fees associated with their services. This means that more of the revenue generated from ad placements goes directly into your pocket, increasing your overall profitability.
3. Customization
Directly uploading assets empowers you to tailor your ad campaigns precisely to your target audiences or specific content genres. You can upload different ad creatives to promote your own content to various viewer segments, maximizing the relevance and effectiveness of your advertising efforts.
Ad Placements
Ad placements refer to the timing and positioning of video advertisements within streaming content.
Pre-roll Ads
Pre-roll ads are video advertisements that play before the main content starts. They typically have a fixed duration and are displayed to viewers before they can access the desired video content.
Pre-roll ads have the advantage of capturing viewers’ attention when they are most engaged, as they are eager to access the main content.
Best practices for pre-roll ads include keeping them concise, relevant, and engaging to prevent viewers from skipping them.
Mid-roll Ads
Mid-roll ads are video advertisements that appear in the middle of the main content, interrupting the viewing experience. They are often inserted at natural break points in longer-form video content, such as during pauses or transitions.
Mid-roll ads provide advertisers with an opportunity to reach viewers during longer-form content, maximizing their exposure.
However, it’s crucial to ensure that mid-roll ads are inserted at appropriate break points to minimize viewer frustration and maintain a seamless viewing experience.
Post-roll Ads
Post-roll ads are video advertisements that play after the main content has ended. They capitalize on the viewer’s engagement with the content by presenting relevant ads immediately after they have consumed the primary content.
Post-roll ads benefit from being displayed immediately after the main content, capitalizing on viewers’ engagement.
However, they risk lower viewer retention as viewers may exit the platform after consuming the main content. To optimize post-roll ads, ensure they are relevant and compelling enough to retain viewers’ attention.
Ad Insertion Methods
Ad insertion methods, such as Client-Side Ad Insertion (CSAI) and Server-Side Ad Insertion (SSAI), are techniques used to deliver advertisements within streaming content. These methods determine how ads are integrated into the video content.
CSAI – Client-Side Ad Insertion
The video player on the client’s device handles the ad insertion process by dynamically inserting the ads into the main content during playback. That is, ad content is delivered separately to the viewer’s device or browser along with the main content.
CSAI allows for more flexibility in ad targeting and personalization since ad decisions can be made in real-time based on user data and behavior.
However, CSAI may be susceptible to ad blockers and can result in buffering or playback issues if the client device has limited processing power.
SSAI – Server-Side Ad Insertion
In SSAI, ad content is integrated into the video stream on the server side before being delivered to the viewer’s device.That is, the ad insertion process occurs within the streaming service’s infrastructure, allowing for greater control over ad delivery and playback.
SSAI ensures a seamless viewing experience by eliminating buffering or playback interruptions associated with client-side ad insertion.
Additionally, SSAI reduces the likelihood of ad blocking since ads are integrated into the video stream itself.
However, SSAI may require more advanced server-side infrastructure and can limit the ability to personalize ads based on client-side data.
Fill Rate
Now that you know the basics of ad tech, it’s time for you to understand fill rates as they determine the profitability of your streaming service. Fill rate, simply put, is the percentage of ad requests that actually result in ads being displayed to viewers.
It is a crucial metric in advertising that indicates the effectiveness of your ad monetization efforts. A high fill rate signifies that a large portion of ad inventory is being utilized, leading to increased revenue potential for publishers
On the other hand, a low fill rate indicates inefficiencies in ad serving, potentially resulting in missed revenue opportunities and underutilized ad inventory.
Calculating Fill Rate
Fill Rate (%) = ( Total Number of Ad Requests ÷ Number of Ad Requests Filled ) × 100
Factors Affecting Fill Rate in AVOD Service
Understanding the factors influencing fill rate is essential for your AVOD service to optimize ad monetization strategies.
From the demand for ad placements to the quality of ad inventory and user engagement levels, various elements play a role in determining the efficiency of ad delivery , and therefore, the fill rate.
1. Ad Demand
The demand from advertisers for ad placements on your streaming service significantly influences the fill rate. Higher demand means more advertisers competing for ad inventory, leading to a higher fill rate.
2. Ad Inventory Quality
The quality and relevance of your ad inventory play a crucial role in fill rate. Advertisers are more likely to bid on high-quality ad placements that align with their target audience and objectives.
3. Content Context
The context in which ads are displayed, such as the genre or topic of the video content, can impact fill rate. Ads that are relevant to the content are more likely to be served, resulting in a higher fill rate.
4. Ad Placement
The placement of ads within the video content also affects fill rate. Ads placed strategically, such as before, during, or after engaging content segments, may have higher visibility and attract more advertiser interest.
5. User Engagement
The level of user engagement with your streaming service and content can influence the fill rate. Platforms with higher user engagement metrics, such as longer watch times or frequent visits, may attract more advertisers and achieve higher fill rates.
6. Technical Infrastructure
The efficiency and reliability of your ad-serving technology can affect the fill rate. Technical issues such as server downtime, slow loading times, or ad delivery errors may result in lower fill rates.
From the Monetization section of the left menu, select Manage Monetization > AVOD (Video Ads) > Manage Campaign.
Click Add New Campaign on the right side of the screen to create your campaign.
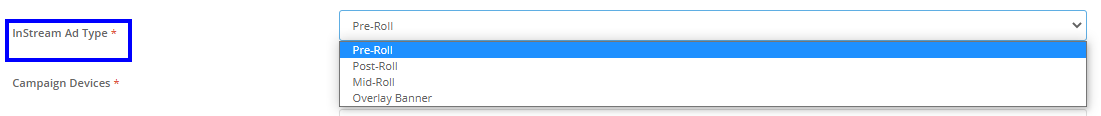
Select Ad type > Pre-roll, Mid-roll, or Post-roll as per your requirement.
Enter Name of the campaign,
Select the Release Order (RO) for this campaign under Campaign RO.
In Ad Asset Type, map the type of asset or tag you have. We support VAST, VPAID, Programmatic tags as well as an asset of the video. Learn more about creating assets.
If you want to direct users to a new URL when they click on the ad, enter the URL in Click-Through URL.
In Campaign Content-Type, decide whether you want to run the ad on On-demand content, live stream content, or both.
Under Secondary Information,> Is Skippable ad? choose if the ad can be skipped by users or not. If yes, add the duration at which the skip should appear under Ad Skip Offset.
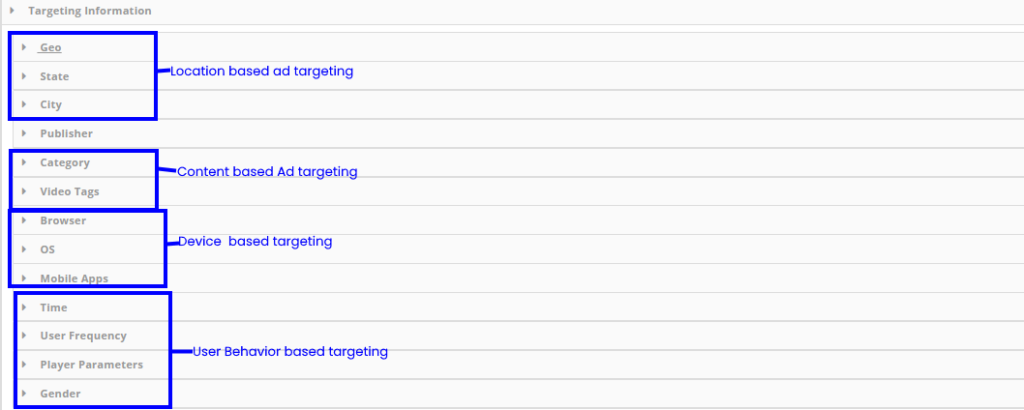
Targeting Information is used for setting the targeting criteria for the ad
Geo-Target ads by countries (eg: US, UK, Canada)
State – Target ads by states (eg: Texas, California)
City – Target ads by cities (eg: New York, Las Vegas)
Category – Target ads by categories (eg: News, Entertainment)
Video Tags – Target ads by specific tags (eg: Joe Biden, Donald Trump). All videos that have these tags will run the ad
Browser – Target ads by browsers (eg: Chrome, Firefox)
OS – Target ads by OS (eg: Mac, Windows 10)
Time – Target ads by days and time (eg: run from 2 pm to 10 pm Monday to Friday)
User Frequency – Target ads by the number of times you want a user to see the ad (eg: 2 times per day)
Player Parameters – Target ads by devices (eg: iOS, Amazon Fire TV)
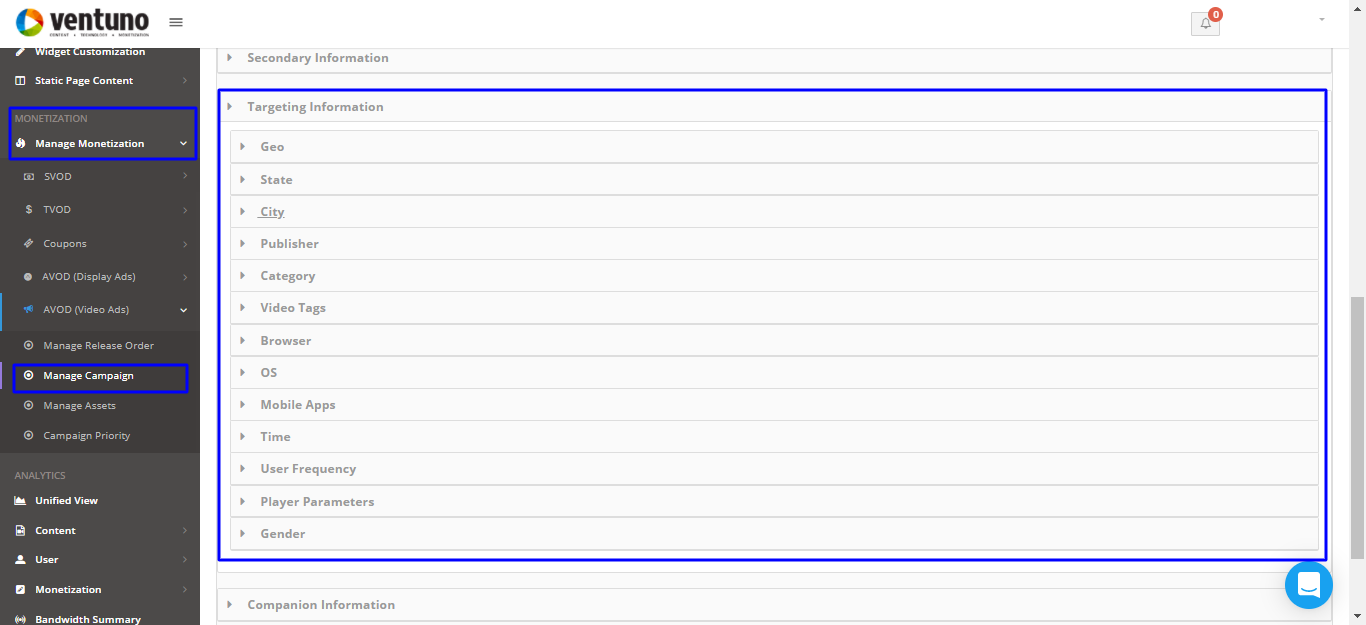
Click Confirm to complete the process.
On the next page click Save Campaign to save the campaign. Click Edit Campaign to edit the campaign details.
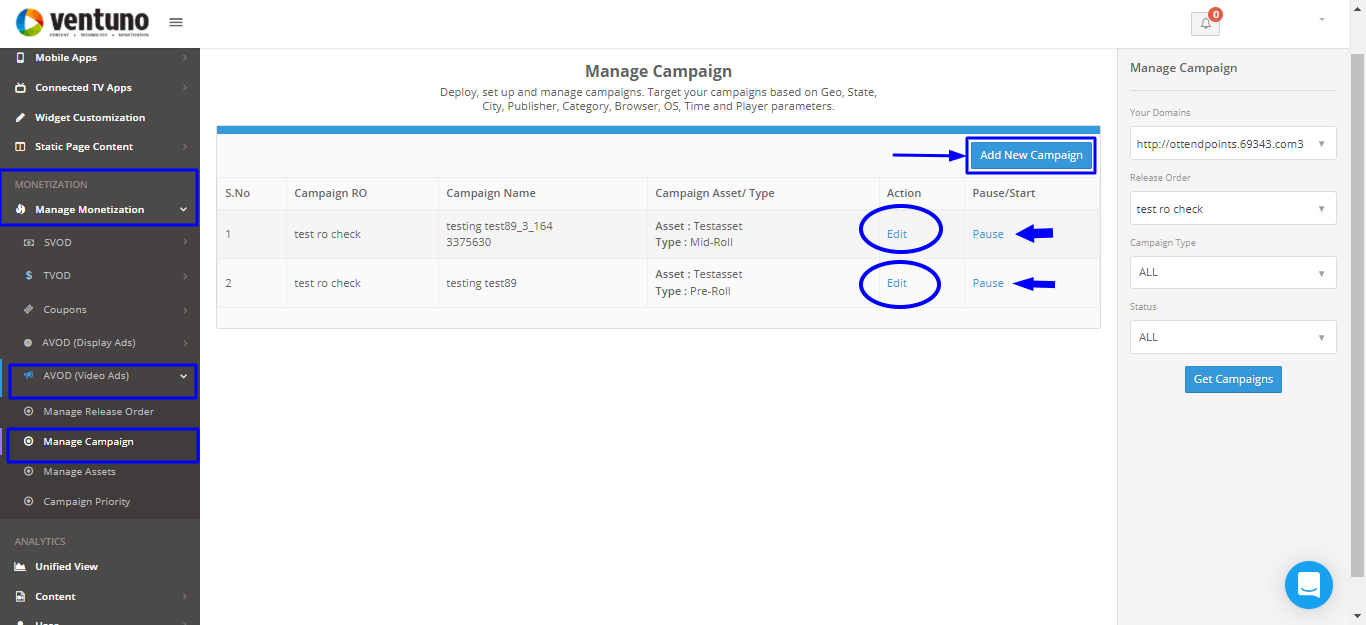
You can also Pause/Start your campaign from this page.
FAQ
Does ad placement within content (e.g., beginning, middle, end) affect performance?
Yes, ad placement significantly impacts performance.
Pre-roll: High viewability but can disrupt viewing flow.
Mid-roll: Less intrusive but potential drop-off during natural breaks.
Post-roll: Lower viewability but good for capturing engaged viewers.
Track metrics like viewability, completion rates, and user feedback to optimize.
What ad formats are performing best (e.g., pre-roll, mid-roll, banners)?
There’s no “one size fits all” answer. It depends on your audience, content, and platform. Test different formats (pre-roll, mid-roll, banners, native) and analyze performance metrics like revenue, completion rates, and user engagement.
Am I using the right ad networks and exchanges?
Monitor performance by network/exchange. Compare fill rates, eCPM, and user experience. Experiment with new options while keeping a core set of reliable partners. Consider industry reports and feedback from other AVOD owners.
What is my eCPM (effective cost per mille) and how can I improve it?
– Relevance: Target the right users through user data, geo-targeting, and contextual targeting.
– Premium Formats: Test interactive or high-impact formats, but balance user experience.
– Optimized Placements: Experiment with ad placement within content for better viewability and engagement.
What targeting options are available and how can I leverage them effectively?
– Demographics: Utilize age, gender, income, and location data for audience segmentation.
– Interests: Target users based on browsing history, app usage, and content consumption.
– Contextual Targeting: Match ads to specific content themes or keywords for increased relevance.
– Dynamic Creative Optimization (DCO): Personalize ad creatives based on user data for improved engagement.
How does the length of content impact ad revenue?
Pros of longer content: More ad breaks = more potential ad impressions and revenue.
Cons of longer content: Risk of user drop-off due to ad interruptions.
Find the sweet spot considering audience preferences, content type, and potential revenue gain. Consider shorter content with higher user engagement and ad completion rates vs. longer content with more ad inventory.
What are the legal and regulatory considerations for AVOD advertising?
Ensure user consent, data storage, and compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
Wrap Up
As the demand for ad-supported video-on-demand (AVOD) services continues to grow, understanding the fundamentals of ad tech is key to maximizing the potential of your streaming service.
Whether it’s enhancing interactive capabilities or ensuring efficient ad serving, understanding and leveraging these tools can make all the difference.
Monitoring and optimizing fill rates is essential for maximizing ad revenue.
As you navigate the complexities of ad tech, consider choosing an all encompassing OTT platform provider like Ventuno. With support for all these features and more, Ventuno can help you stay ahead of the curve and make the most of your streaming service.





